Digital Projectors have been an indispensable part of every educational institute, auditorium, seminar hall, conference room, and office for decades. Existing in a variety of forms, digital projectors are used for multiple purposes ranging from conducting classroom lessons, conferences, meetings, seminars and even for infotainment at times. However, different areas of application require different types of digital projectors. For example, in cinema halls, high-resolution laser projectors because it requires heavy-duty performance on a very large screen. On the other hand, a simple Pico projector can make do in a small classroom of around 15 students.

In the world of projection technology, there are four main types including; DLP, LCD, LED and LCOS. DLP stands for Digital Light Processing, LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display while LCOS means Liquid Crystal on Silicon. Also, there are laser projectors that rely on solid-state laser instead of lamp for its light source. Different types of projectors serve different types of areas of application and have a varied range in terms of price. Thus when choosing a projector, one has to be aware about their requirements and the budget they have in their mind.
In this blog post, we will discuss in details about the different types of projectors in the market, technology they use and their uses.

Types of Digital Projectors
There are multiple type of Digital Projectors depending upon the technology they deploy to produce an image on the projector screen. The different types of Digital Projectors are given below:
- DLP Projector
- LCD Projector
- LED Projector
- LCOS Projector
- CRT Projector
What is DLP Projector?
As we discussed above, DLP stands for Digital Light Processing Projector which makes use of tiny mirrors that reflect light towards the screen. The setup includes a physical colour wheel that spins to generate sequential colours. DLP projectors can be single-chip or three-chip with red, green and blue DLP chips.
The light output of the DLP projectors is vibrant and highly suitable for environments with ambient lightings like classrooms and conference rooms.
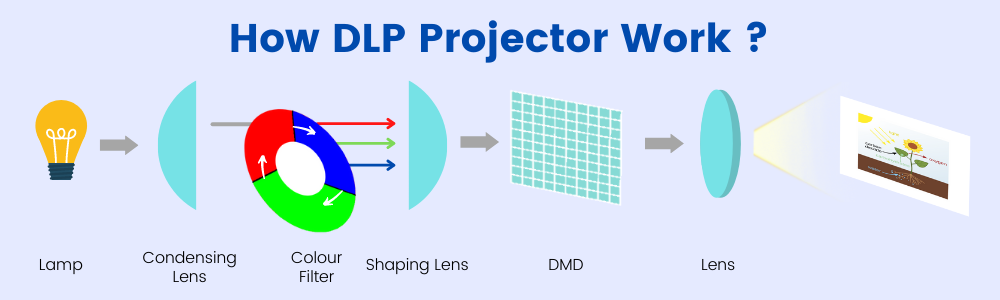
DLP Projector: How it Works?
DLP projector consists of a chip that is made up of millions of microscopic mirrors, each of which is capable of independent adjustment. They can move towards or away from the light source to create a light or dark pixel. To create coloured images, the colour wheel rotates in order to create coloured pixels on the screen. Thus, the colours are displayed sequentially at a high rate than an observer sees a full coloured image. Most of the systems operate at up to 10x the frame rate.
Advantages of DLP Projector
- It offers vibrant coloured images with high contrast.
- Since the space between the component micro-mirrors is <1 micron, the resultant images are sharper with lesser space between the pixels.
- Minimal light loss and maximum light output.
- Deeper blacks as compared to other projection technologies.
Disadvantages of DLP Projector
- Prevalent rainbow effect.
- It has limited numbers of pixels.
- Lesser brightness as compared to LCD projectors.
- Produces brief flashes across the screen that can be a disturbance.
DLP Projector Uses
DLP Projectors are used for the following purposes in our home, school, and offices.
- Used a business projector for conducting conferences and delivering presentations.
- Used in home theatres for displaying movies, TV programs, playing video games, etc.
- Used in command and control centers by telecommunications and utility companies.
- In classrooms and hotels for lectures and launch events.
LED Projector: How it Work?
LED projectors use the LED lamps as it light source. LED lights work on a process called electroluminescence to produce light. In the source lamp, electricity passes through the semiconductor material that the LEDs are made up of. It allows a certain types of energy to pass through them. When an electrical energy passes through the material, it kicks off electrons that are too big to pass through. They shrink and give off protons which are the constituting particles of light.
This process generates very less amount of heat as compared to the traditional gas-filled lamps. This lengthens the life of a LED lamp as compared to the regular lamps.
In LED projectors, there are arrays of red, green and blue LEDs. They are arranged in combinations to give a very accurate white light. This light is then reflected on hundreds of tiny mirrors. In other words, the working of an LED projector is similar to the LCD and DLP projector except for the lamp used.
There are several advantages of using an LED projector. There is lesser sound and heat during its operation. The combination of colour LEDs results in better white light than most of the traditional lamps. This is why LED projectors have better ability to produce a wide array of colours than of the other projectors.
Advantages of LED Projector
- LED projectors use LEDs to produce images. As we know LEDs are more light efficient as compared to the incandescent light bulbs.
- LED projector can produce light of any colour without using any colour filters.
- LED projectors are small and convenient to be moved around.
- LED projector takes much lesser time to be set up.
- They can be frequently turned on/off as compared to DLP projector, LCD projector.
- LED Projectors very less amount of health.
- LED projectors fail gradually instead of abrupt failure like DLP and LCD.
- LEDs have longer lamp life and lower cost of replacements.
Disadvantages of LED Projector
- Initial price of LED Projectors is high.
- LED projector depends on ambient temperature. They require optimum temperature to operate.
- LED Projectors require current-regulated supply to function properly.
- LEDs emit light only with correct electrical polarity.
- Blue light pollution.
LED Projector Uses
LED projectors find utility in almost the same place as the LCD or DLP projector does. Here are some of the most common application areas.
- Classrooms
- Dorm rooms
- Home theatres
- Conference Rooms
What are LCD Projector?
LCD or Liquid Crystal Display is another common technology used in projectors. LCD Projectors use the same liquid crystal display technology that can be found in televisions and monitors as well. An LCD Projector creates images using multiple elaborate steps. They consist of three LCD panels which cast image using the three primary colours; red, green and blue. All three of the colours are simultaneously projected so that the image is completely coloured.

LCD Projector: How Does It Work?
LCD Projectors use three liquid crystal displays, in which an image is created through multiple steps. A light source emits a beam of white light which is passed to three mirrors which are specially shaped to reflect only particular wavelengths of light. Each coloured light beam is sent to an LCD panel, which receives an electrical signal. The signal commands the panel on how to arrange the pixels in the display to create the image. The same image is produced on the three LCD panels, but in different colours due to the source light falling on them. These different coloured images are then combined in a prism resulting in a single coloured image. Finally, the image goes through a lens before reflecting on the projection screen.
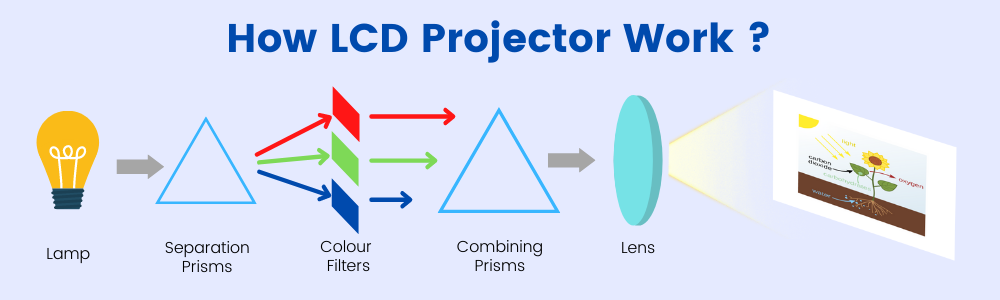
Advantages of LCD Projector
- LCD Projector is more light efficient as compared to the DLP projectors.
- LCD produces brighter images as compared to other projection technologies.
- Produce more beautiful and vibrant colours even in a brightly lit room.
- LCD projector produces sharper and focussed images.
Disadvantages of LCD Projector
- It produces chicken wire project making images look too much stuffed with pixels.
- LCD Projector is heavier and is inconvenient to be moved around.
- Produces dead pixels over the time.
- Replacements of LCD Projectors are expensive. They are also prone to burn out quickly.
LCD Projector Uses
LCD Projectors are highly used in the following areas:
- Schools
- Corporate Presentations
- Exhibitions and Tradeshows
- Home Theatres
CRT Projector
CRT Projectors were commonly used technology during the early days. It deploys a small high brightness cathode ray tube (Hence the projectors are called CRT, Cathode Ray Tube projectors). The first colour CRT Projector was invented in early 1950s. In this type of projector, the red, green and blue parts of the video signal are processed and sent to the individual CRTs whose images are focused by the projector lenses to obtain the overall image. Recently, they have been replaced by other technologies like LCD Projectors, DLP Projectors, LED Projectors for their cost-effectiveness and convenience.
Advantages of CRT Projector
- Long operational life.
- Good brightness
- Rare bulb replacements
- High resolution
- Superior overall black level
- Zero input lag as well as zero motion blur
Disadvantages of CRT Projector
- They are large and heavy as compared to other contemporary projectors.
- They require long hours to be set up.
- Absolute ANSI brightness is far lesser than the contemporary DLP, LCD technologies.
- Suffers from colour divergence and geometric distortions.
- Consume more power.
- They are more prone to burn-in.
LCoS Projector
LCoS stands for Liquid Crystal on Silicon which is a variation of LCD technology. Just like LCD projectors, LCoS Projector split the light into red, green and blue components and direct them to three separate LCD-based imagers. However, the light first reflects off a shiny surface behind the cell array instead of simply passing through LCD cells.
White lamps are used as the light source in LCoS Projectors. Some of the LCoS projectors use blue laser and yellow phosphor for the light source.
How Does LCoS Projector Work?
LCoS Projectors use three LCOS chips to modulate light in red, green and blue channels each. However, unlike DLP Projector, it doesn’t have a spinning colour wheel. The LCoS technology is usually high in resolution and even higher in price.
Advantages of LCoS Projector
- Inherent high resolution
- Pixel edges are smoother as compared to DLP Projectors
- More natural and life-like images.
- LCoS Projector delivers continuous red, green and blue simultaneously.
- No rainbow effects, eye strain or headache as compared to DLP Projector.
Disadvantages of LCoS Projector
- Low contrast ratio.
- Responds negatively to ambient lighting.
- Limited lamp life of 1000-1500 hours.
- Replacements are expensive.
Uses of LCoS Projector
- Near-to-eye viewing systems.
- Optical beam steering
- Micro projectors
- Holographic projectors
Globus’ line-up of Digital Projectors includes DLP Projectors of Ultra Short Throw, Short Throw, Long Throw, and Portable Projector type. It speaks of high resolution, contrast ratio, brightness, lamp life, and long operational life. Globus Digital Projectors are an essential component of the Digital Teaching System that includes an Interactive Board with multi-touch support.


9 Item(s)
caroline smith
Dharmu
richardson owino
Tanima Chandra
Preetika Kapoor
Dr. Abhinav Setya
Mrs Priyanka Kumaar
Mr. Pranay Mishra
Mrs Anita Sahani
9 Item(s)